In the realm of inflammation resolution, a groundbreaking area of research has emerged, shedding light on the role of pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPMs) in orchestrating the delicate balance between immune response and resolution. SPMs, derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids, exhibit potent anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving properties, representing a promising avenue for therapeutic interventions. In this article, we will explore the significance of pro-resolving lipid mediators, their mechanisms of action, and their potential implications for treating inflammatory disorders.
The Origins of Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators:
Derived from essential fatty acids such as omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, pro-resolving lipid mediators are enzymatically produced during the inflammatory process. Resolvins, protectins, and maresins are prominent members of this lipid mediator family, each playing a unique role in orchestrating the resolution of inflammation. These specialized molecules act as “off-switches” for inflammation, promoting the removal of inflammatory cells and facilitating tissue repair.
Mechanisms of Action:
SPMs exert their anti-inflammatory effects through intricate molecular mechanisms that involve interactions with specific receptors and modulation of immune cell activity. Resolvins, for instance, bind to G protein-coupled receptors, initiating signaling pathways that dampen inflammatory responses. Protectins are known for their ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines and promote the clearance of apoptotic cells, contributing to a swift resolution of inflammation. Maresins, on the other hand, play a crucial role in tissue regeneration by enhancing tissue repair processes.
Potential Therapeutic Applications:
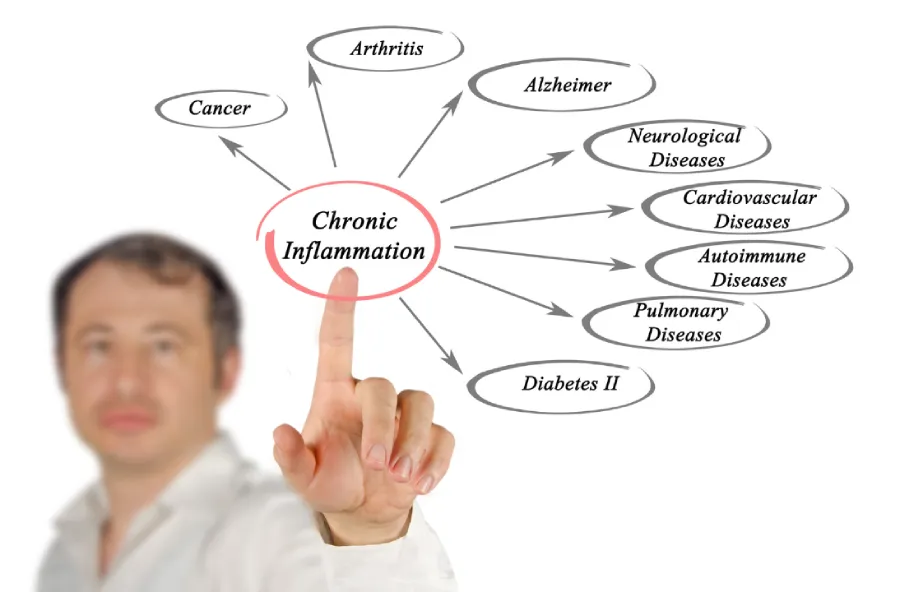
The unique properties of pro-resolving lipid mediators have spurred interest in their therapeutic potential for various inflammatory disorders. Chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and atherosclerosis, could benefit from interventions that enhance the resolution of inflammation. By promoting the timely removal of inflammatory cells and the restoration of tissue homeostasis, SPMs offer a novel approach to managing these diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While the therapeutic potential of pro-resolving lipid mediators is exciting, challenges remain in translating these findings into clinical applications. Developing stable analogs, improving delivery methods, and understanding the precise mechanisms underlying their actions are critical aspects that warrant further investigation. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges, paving the way for the development of targeted therapies harnessing the power of pro-resolving lipid mediators.
In conclusion, pro-resolving lipid mediators represent a fascinating frontier in the field of inflammation resolution. With their ability to fine-tune immune responses and promote tissue repair, these molecules hold great promise for revolutionizing the treatment of inflammatory disorders. As research continues to unravel the complexities of SPMs, we can anticipate the emergence of innovative therapeutic strategies that harness the natural power of our body’s resolution mechanisms to combat inflammation.